It sounds simple, but even as a Groovy practitioner I still forget how it works. Maybe this one is a note-to-self if anything.
Map Variables
A Map in Groovy is a collection of key-value pairs, similar to a dictionary or lookup table. It is very useful when you need to collect values based on specific intersection and use it later.
Examples:
- Collect Life in Months by asset class and apply the default value when adding a new asset line
- Collect the SOFR rate and apply it to a loan product’s average balance based on the selected SOFR SmartList value
Let’s take a look at the first example:
//Define Map
def LifeInMnths = [:] as Map<List,List>
def tmpMembers = []
//Assign CPX to cube
Cube cube = operation.application.getCube("Cube_CPX")
//Build Source grid
def sourcebuilder = cube.flexibleDataGridDefinitionBuilder()
sourcebuilder.setSuppressMissingBlocks(true)
sourcebuilder.setSuppressMissingRows(true)
//Set Source grid POV
sourcebuilder.setPovDimensions('Scenario','Version','CostCenter','Project','Asset Class','Years')
sourcebuilder.setPov('Fcst','Working','C00000','No_Project','Lvl0Descendants(Total_Asset_Class)','No Year')
//Set Source grid Col
sourcebuilder.setColumnDimensions('Entity')
sourcebuilder.addColumn('ENT_0001')
//Set Source grid Row
sourcebuilder.setRowDimensions('Account','Period','Asset Detail')
sourcebuilder.addRow('LifeinMonths','BegBalance','No_Asset_Detail')
//Load Grid
cube.loadGrid(sourcebuilder.build(),false).withCloseable{sourcegrid ->
if(sourcegrid){
GridIterator sourceitr = sourcegrid.dataCellIterator()
sourceitr.each{
tmpMembers = [it.getMemberName("Asset Class")]
LifeInMnths[tmpMembers] = [it.data]
println tmpMembers + LifeInMnths[tmpMembers]
}
}
}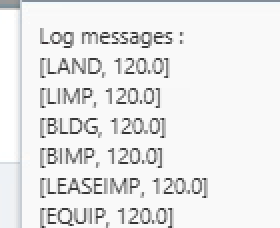
Once you have collect the Life in Months by Asset Class value, you can apply it to the intersection when you add a new line.
LifeInMnths.each{k,v ->
if(k[0] == 'LAND')
targetgridbuilder.addRow(['Life_in_Months',LAND],[v[0]]);
}Of course, you wouldn’t hardcode ‘LAND’ in your grid… but you get the point. You can use RTP to pick up the Asset Class that the user wants to add and write the value into the intersection.
What about the second example:
//Define Map
def ADBMap = [:] as Map<List,List>
def RateSelectionMap = [:] as Map<List,List>
def RateMap = [:] as Map<List,List>
def tmpMembers = []
//Assign FS to cube
Cube cube = operation.application.getCube("Cube_FS")
//Build Source grid
def sourcebuilder = cube.flexibleDataGridDefinitionBuilder()
sourcebuilder.setSuppressMissingBlocks(true)
sourcebuilder.setSuppressMissingRows(true)
//Set Source grid POV
sourcebuilder.setPovDimensions('Scenario','Version','Years','Entity')
sourcebuilder.setPov('Fcst','Working','FY25','ENT_0001')
//Set Source grid Col
sourcebuilder.setColumnDimensions('Period')
sourcebuilder.addColumn('Lvl0Descendants(YearTotal)')
//Set Source grid Row
sourcebuilder.setRowDimensions('CostCenter','Product','Account')
sourcebuilder.addRow('C00000','No_Product','Lvl0Descendants(Input_Rate)')
sourcebuilder.addRow('C00000','Lvl0Descendants(Loans)','ADB')
sourcebuilder.addRow('C00000','Lvl0Descendants(Loans)','Rate_Selection')
//Load Grid
cube.loadGrid(sourcebuilder.build(),false).withCloseable{sourcegrid ->
if(sourcegrid){
GridIterator sourceitr = sourcegrid.dataCellIterator()
sourceitr.each{
if(it.getMemberName("Account") == "ADB"){
tmpMembers = [it.getMemberName("Account"),it.getMemberName("Years"),it.getMemberName("Period"),it.getMemberName("Product")]
ADBMap[tmpMembers] = [it.data]
}else if(it.getMemberName("Account") == "Rate_Selection"){
tmpMembers = [it.getMemberName("Account"),it.getMemberName("Years"),it.getMemberName("Period"),it.getMemberName("Product")]
RateSelectionMap[tmpMembers] = [it.formattedValue]
}else{
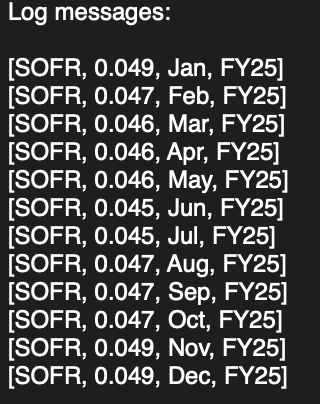
tmpMembers = [it.getMemberName("Account"),it.getMemberName("Years"),it.getMemberName("Period")]
RateMap[tmpMembers] = [it.data]
println tmpMembers + RateMap[tmpMembers]
}
}
}
}
Once you collected the rates, you can apply it to the average balance. You can use IF conditions to match the period and year. In addition, if rate is a driver (SmartList), you can match the driver then calculate the result.
// Create new map to store calculated values
def adbCalculatedMap = [:] as Map<List,List>
// Iterate through ADBMap to find matching rates
ADBMap.each { adbKey, adbValue ->
// adbKey format: [Account, Years, Period, Product]
def adbAccount = adbKey[0]
def adbYears = adbKey[1]
def adbPeriod = adbKey[2]
def adbProduct = adbKey[3]
def adbAmount = adbValue[0]
// Find the rate selection for this product
RateSelectionMap.each { rateSelKey, rateSelValue ->
// rateSelKey format: [Account, Years, Period, Product]
if (rateSelKey[1] == adbYears && rateSelKey[2] == adbPeriod && rateSelKey[3] == adbProduct) {
// Get the selected rate account
def selectedRateAccount = rateSelValue[0]
// Find matching rate in RateMap
RateMap.each { rateKey, rateValue ->
// rateKey format: [Account, Years, Period]
if (rateKey[0] == selectedRateAccount && rateKey[1] == adbYears && rateKey[2] == adbPeriod) {
def rateAmount = rateValue[0]
// Calculate interest: ADB * Rate
def calculatedInterest = (adbAmount as double) * (rateAmount as double)
// Store in new map with key: [Product, Years, Period, RateAccount]
def newKey = [adbProduct, adbYears, adbPeriod, selectedRateAccount]
adbCalculatedMap[newKey] = [calculatedInterest]
}
}
}
}
}In this example, I have “SOFR” in every period for the sake of easiness. In reality, you will likely store it in BegBalance.
I hope this is helpful as always.
Leave a comment